Sometimes “application extension” files (.DLL or .OCX) must be manually registered to properly support the functions of a program. Various errors such as ActiveX, automation or runtime errors can occur when the associated application extension files (also called ActiveX controls) are not registered in Windows for use by the requesting program.

Register 32 or 64-bit DLLs in Windows 10
If you need to register a DLL due to damage or an installation error, you can do so manually using the method described below.
The Regsvr32 tool is a command line program that can be used to register and unregister OLE controls, such as DLL and ActiveX (OCX) controls, in the Windows operating system. If you find that some of your Windows features are working properly, you may need to register your dll files. This tutorial shows you how to register or unregister a dll file using the built-in Regsvr.exe file or some free registration dll tools.
- First click Start, then click Run.
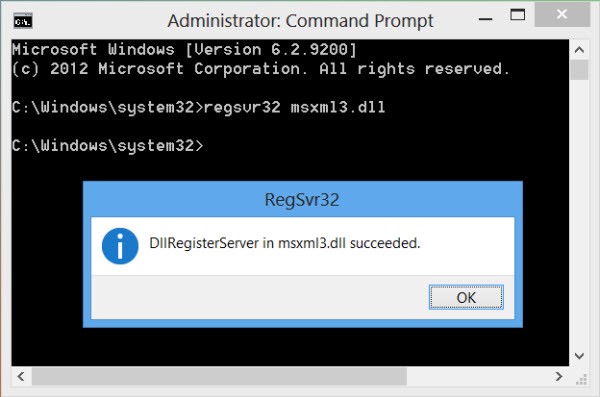
- Now, to save a DLL file, just type the command regsvr32, followed by the path to the DLL file.
- regsvr32 /u “dll path & filename
- Now click OK and you should receive a confirmation message that the DLL has been successfully registered.
- Your DLL has now been successfully registered and can be used by Windows programs. Note that if you receive an error message, you may be using the 64-bit version of the command and not the 32-bit version. If you have installed a 64-bit version of Windows and the DLL is 32-bit, you must run the command with the 32-bit version of regsvr32 :
%systemroot%\SysWoW64\regsvr32
Unregister the DLL File
- To unregister a dll or ocx file, as the administrator, open a command prompt window, type the following, then press Enter :
- regsvr32 /u “Path and filename of the dll or ocx”.
This saves or un-saves the dll file.
Alternatives
Saving a DLL file will not solve all the problems it poses. Sometimes the DLL file is not the cause of the problem, but only the way it manifests itself. The problem may be in the library itself or in the application. In this case, you should try to uninstall and reinstall the application or remove and install the library that uses it.
It may also be useful to update the library if a newer version is available. Finally, make sure that the version of the library is the right one for the application. You can check the application requirements to determine which libraries or frameworks are needed to run the application.
https://support.microsoft.com/en-us/help/844592/how-to-register-a-dll-file

